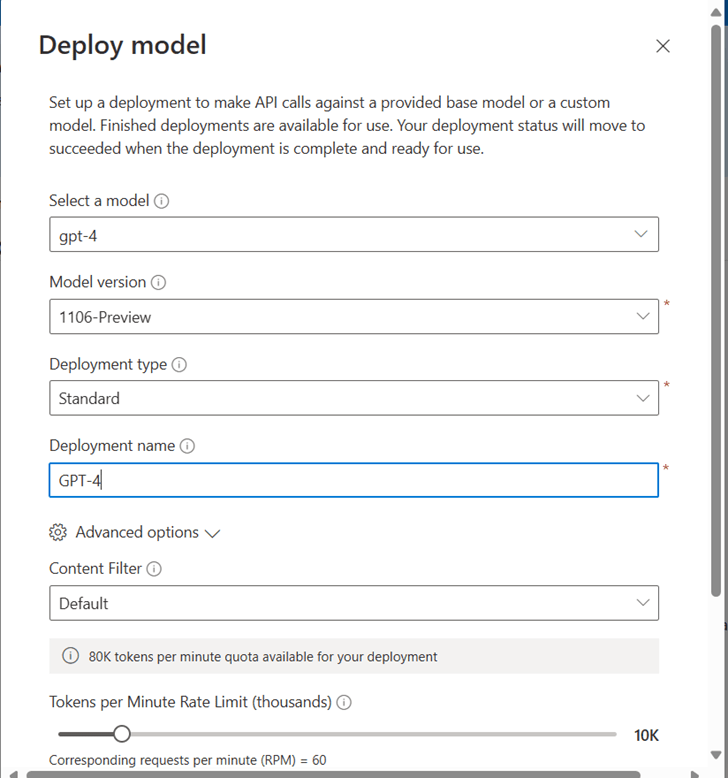
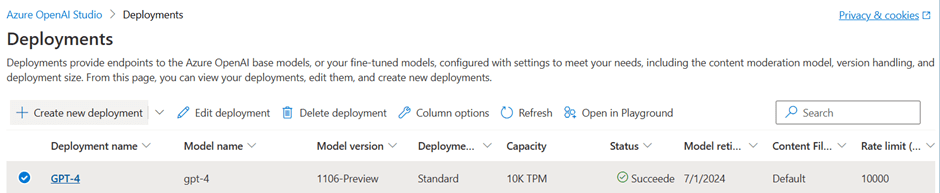
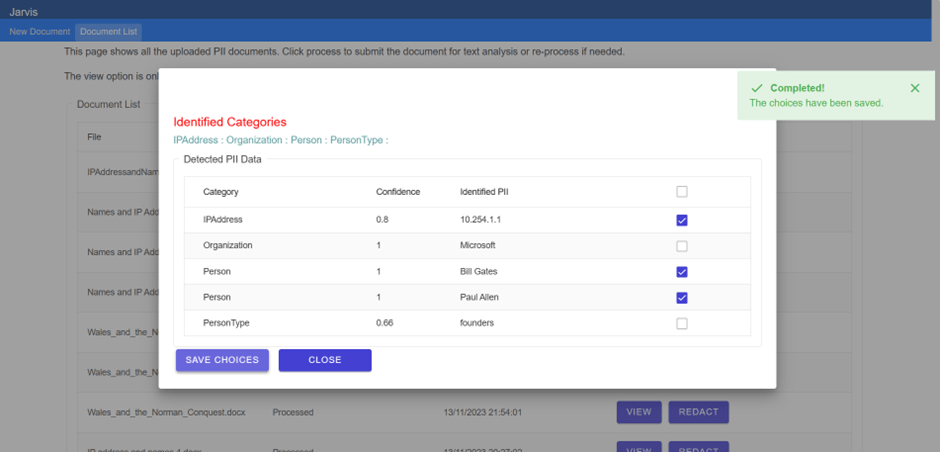
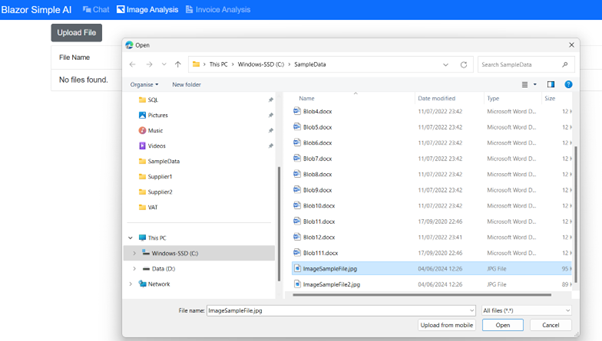
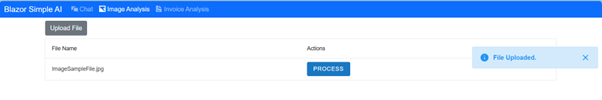
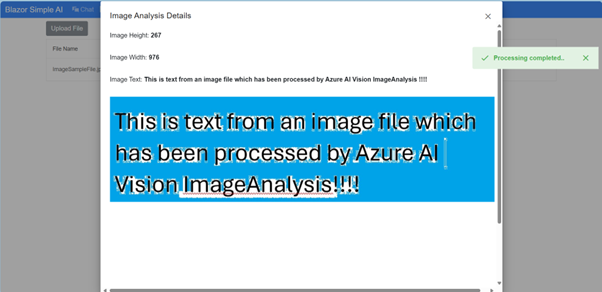
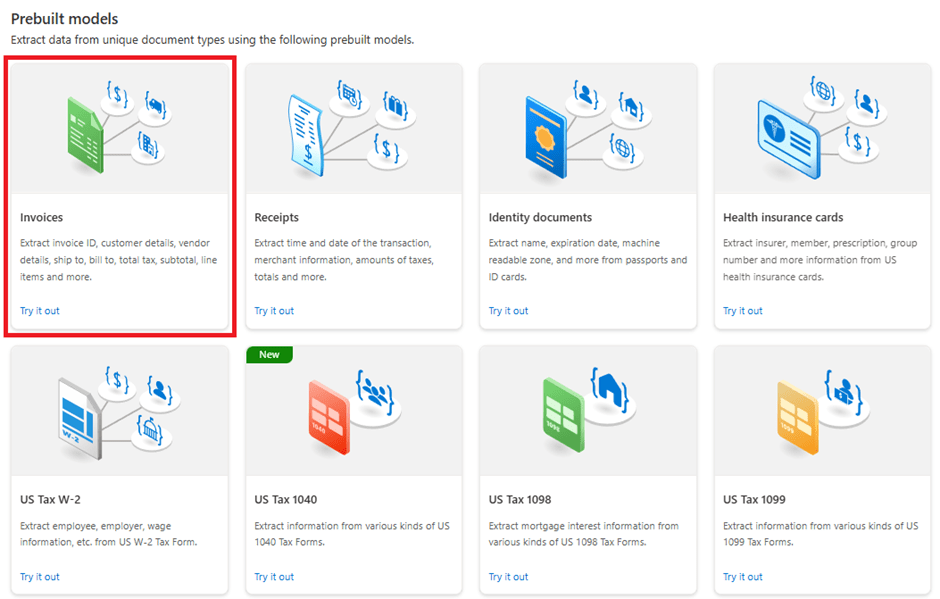
Welcome to the Blazor Simple AI Single Page App, Part 4 of the Microsoft AI services journey, which now includes invoice analysis which utilises Microsoft Azure AI Document Intelligence service. The document Intelligence service is used to extract the text from an invoice using a pre-built model. A sample of some of the models is shown below in document intelligence studio.
This document explains the project in my GitHub repository which is available here: https://github.com/tejinderrai/public/tree/main/BlazorSimpleAI.
If you would like to download the whole series of posts for the Blazor Simple AI Project, you can download the PDF here.
Since part 3, the following nuget packages have been added to the project.
Azure.AI.DocumentIntelligence (Pre-release)
New Components
Three components have been developed for the image analysis. These are as follows:
- InvoiceLoader.Razor – A component which includes the child component (InvoiceFileList.Razor), which uploads invoices to Azure blog storage container
- InvoiceFileList.Razor – A component which lists the invoices that a present in the invoice upload container
- InvoiceViewer.Razor – A component which allows the user to view the uploaded invoice in a dialog
Provisioning a Microsoft AI Document Intelligence Service
To provision a Microsoft AI Document Intelligence Service resource, follow the instructions in the article below.
Learn about Microsoft AI Document Intelligence
To learn more about the capabilities of Microsoft AI Document Intelligence capabilities, see. Document Intelligence documentation – Quickstarts, Tutorials, API Reference – Azure AI services | Microsoft Learn. Microsoft Azure AI Document Intelligence includes more analysis capabilities, not just specifically an invoice model.
Configuration Settings Changes
The following configuration settings were added to appsettings.json.
“AzureDocumentIntelligenceConfig”: {
“AzureDocumentIntelligenceKey”: “[Your Azure Document Intelligence Key]”,
“AzureDocumentIntelligenceEndpoint”: “[Your document intelligence endpoint https://[Resource Name].cognitiveservices.azure.com/”
},
“AzureStorageConfig”: {
“AzureStorageInvoiceContainer”: “[Your Invoice Upload Container Name]”,
“AzureStorageInvoiceProcessedContainer”: “[Your Invoice Processed Container Name]”, },
The invoice processed container is the output interface file that is generated from the text extracted from the original invoice file. It is an output of JSON which utilises the InvoiceAnalysisData data type.
Note: Whist this project utilises the service key, in an enterprise environment, you must consider using token based access to the service secured by Microsoft Entra ID, or if you wish to utilise the service key for any reason, utilise Azure Key Vault to protect the key used by the application with a managed identity for the application to access the service key stored in Azure Key Vault.
Components
Invoice Loader Component (InvoiceLoader.Razor)
The invoice upload component utilises Blazor InputFile for the user to select the file to upload in the application. The component reads the Azure Storage connection string from the configuration, including the container, then uploads the file to the container and also adds a blob http header for the file content type taken from the file properties. The Radzen notification service is used to notify the user of the application activities. I also included a basic spinner as part of the interaction for the upload process.
Invoice File List Component (InvoiceFileList.Razor)
This component reads the Azure Storage connection string from the configuration, including the container, then displays the invoice blob file names in a Radzen DataGrid. A button is added to view the invoice, or process the invoice, which then calls the Radzen notification service to display the activities being taken by the application.
Invoice Viewer Component (InvoiceViewer.Razor)
This component is a child component displayed in a Radzen dialog box which displays the original uploaded invoice directly from the Azure blob storage invoice upload container. A storage SAS key is generated which provides time limited access to the user in order for the invoice to be displayed in the dialog.
Data Classes
InvoiceAnalysisData.cs – The class for the invoice.
InvoiceItem.cs – The class for the invoice items.
Invoice Sample
I have created an invoice samples to test the pre-built invoice model from Microsoft Azure Document Intelligence.
Supplier 1 Invoice (PDF)
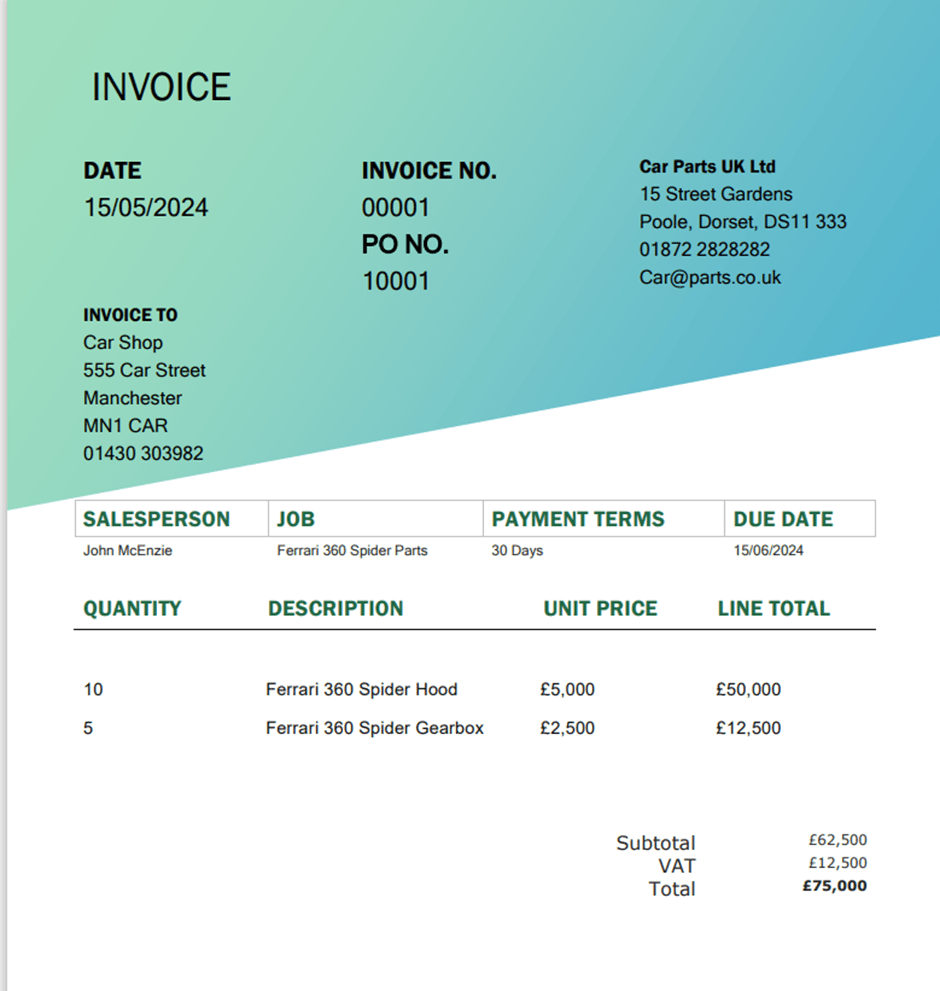
I created two additional sample invoices, both of which were tested and successfully processed. I have not covered the upload of these in my blog post.
Supplier 2 – Jpeg image
(Missing Quantity)

Invoice 3 – Handwritten Invoice – jpeg image
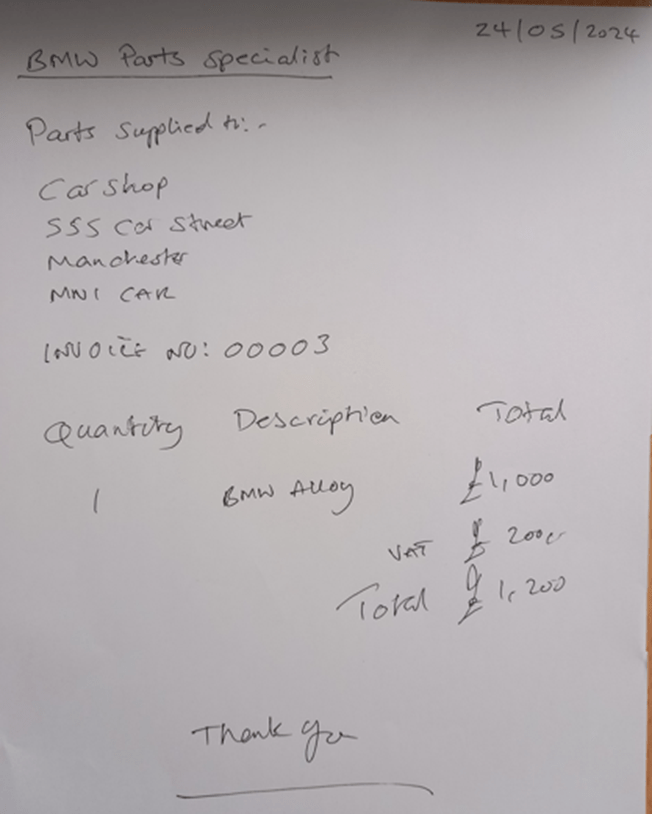
The UI
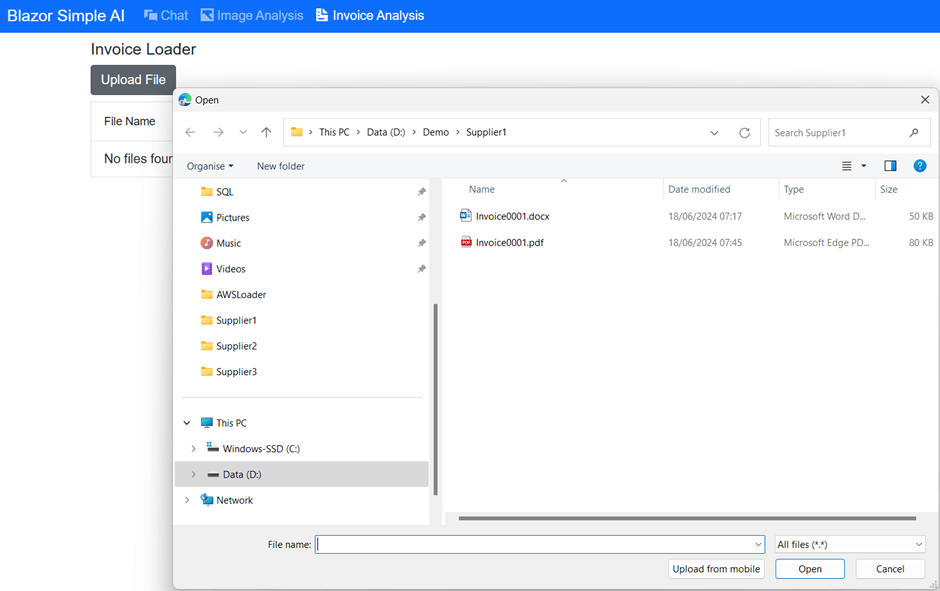
The UI for invoice analysis is as follows.
Invoice Analysis

Upload File

View Button – Opens the PDF in a dialog box

Process Button – Interactive Dialog box

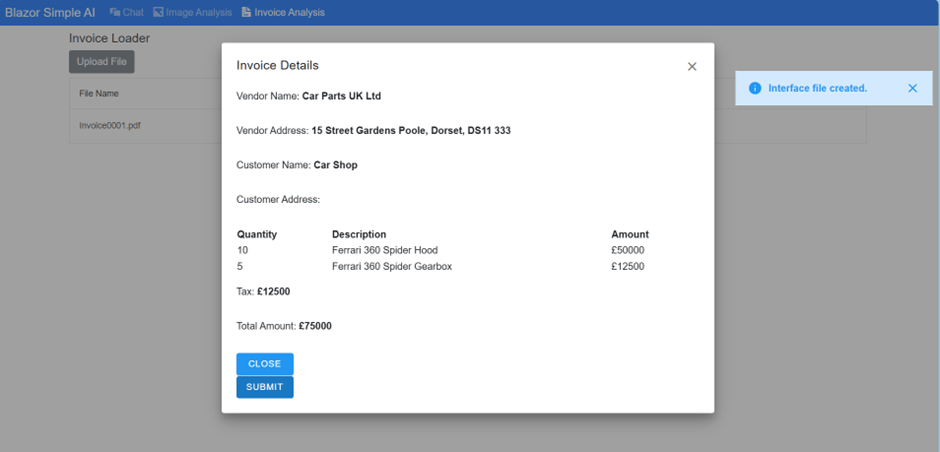
Processing Completed – Invoice details – text extracted into InvoiceAnalysis object.

Submit Button – Create an output interface file in JSON format.
Azure Storage – (invoiceanalysisupload container)

Processed Output file

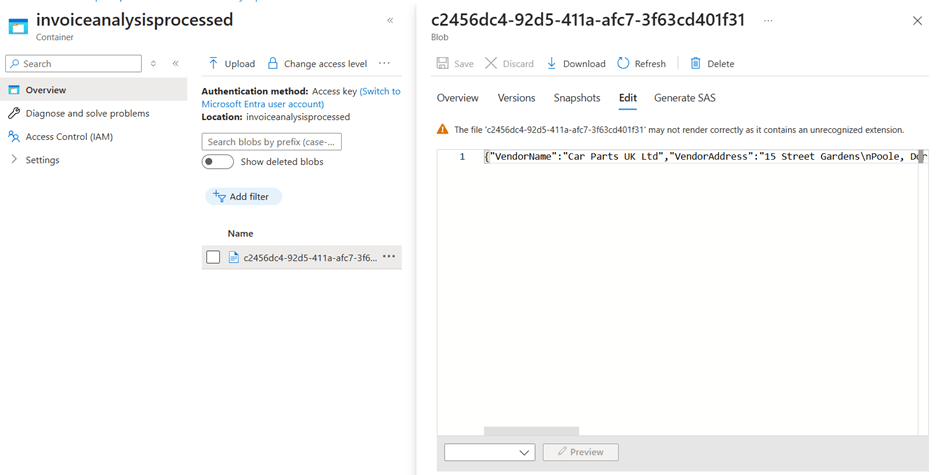
File Contents
{
"VendorName":"Car Parts UK Ltd",
"VendorAddress":"15 Street Gardens\nPoole, Dorset, DS11 333",
"CustomerName":"Car Shop",
"CustomerAddress":null,
"InvoiceItems":[
{"Quantity":10.0,"ItemDescription":"Ferrari 360 Spider Hood","Amount":"50000"},
{"Quantity":5.0,"ItemDescription":"Ferrari 360 Spider Gearbox","Amount":"12500"}
],
"Tax":"12500",
"InvoiceTotal":"75000"
}Note: The code does not extract the customer address, but this is in fact possible.
The handwritten jpeg image, the second invoice as a jpeg image and the PDF all proved to have 100% extraction using the Microsoft AI Document Intelligence service. That’s just amazing!
It is as simple as that!
The reason for creating a interactive SPA as a sample app, is to demonstrate the features. The same code can be used in event driven architectures, or scheduled triggers. That will be something I will post next.
Invoice 2 – jpeg output
Invoice 2- viewer

Invoice 2 – Processed

Invoice 3 – Handwritten jpeg